
PRINCIPLE 3: Assessment of older people with confusion
Older people who are confused will be assessed. The cause of their confusion will be investigated to determine the appropriate management.
Assessment of older people with confusion
Older people are at increased risk of developing confusion while in hospital. In most cases confusion is due to dementia, delirium or depression.
- Dementia is the umbrella term for a variety of diseases characterised by impairments of brain function, including memory, language, perception and cognitive skill. Older persons with dementia may develop delirium superimposed on dementia.
- Delirium is a common clinical syndrome characterised by confusion and inattention. A person with delirium may also present with a wide variety of bodily illnesses. Other symptoms can include disorientation, emotional fluctuations (such as mood swings), varying levels of consciousness, hallucinations, and delusions.
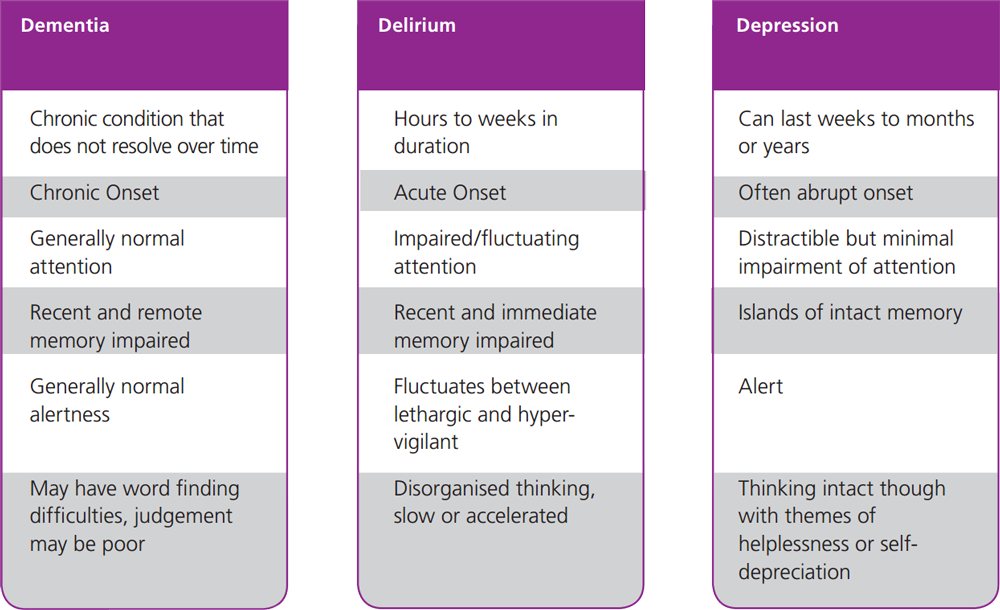
Identifying the cause of confusion
Identifying the cause of a patient’s confusion will determine the most appropriate management options.